Industry 4.0 is a name given to the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of things, cloud computing and cognitive computing. Industry 4.0 is commonly referred to as the fourth industrial revolution.
Industry 4.0 fosters what has been called a “smart factory”. Within modular structured smart factories, cyber-physical systems monitor physical processes, create a virtual copy of the physical world and make decentralized decisions. Over the Internet of Things, cyber-physical systems communicate and cooperate with each other and with humans in real-time both internally and across organizational services offered and used by participants of the value chain.

First came steam and the first machines that mechanized some of the work our ancestors did. Next was electricity, the assembly line and the birth of mass production. The third era of industry came about with the advent of computers and the beginnings of automation, when robots and machines began to replace human workers on those assembly lines.
And now we enter Industry 4.0, in which computers and automation will come together in an entirely new way, with robotics connected remotely to computer systems equipped with machine learning algorithms that can learn and control the robotics with very little input from human operators.
Industry 4.0 introduces what has been called the “smart factory,” in which cyber-physical systems monitor the physical processes of the factory and make decentralized decisions. The physical systems become Internet of Things, communicating and cooperating both with each other and with humans in real time via the wireless web.
For a factory or system to be considered Industry 4.0, it must include:
- Interoperability — machines, devices, sensors and people that connect and communicate with one another;
- Information transparency — the systems create a virtual copy of the physical world through sensor data in order to contextualize information;
- Technical assistance — both the ability of the systems to support humans in making decisions and solving problems and the ability to assist humans with tasks that are too difficult or unsafe for humans;
- Decentralized decision-making — the ability of cyber-physical systems to make simple decisions on their own and become as autonomous as possible.
Nine Technologies Transforming Industrial Production
Advanced digital technology is already used in manufacturing, but with Industry 4.0, it will transform production. It will lead to greater efficiencies and change traditional production relationships among suppliers, producers, and customers—as well as between human and machine. Nine technology trends form the building blocks of Industry 4.0.
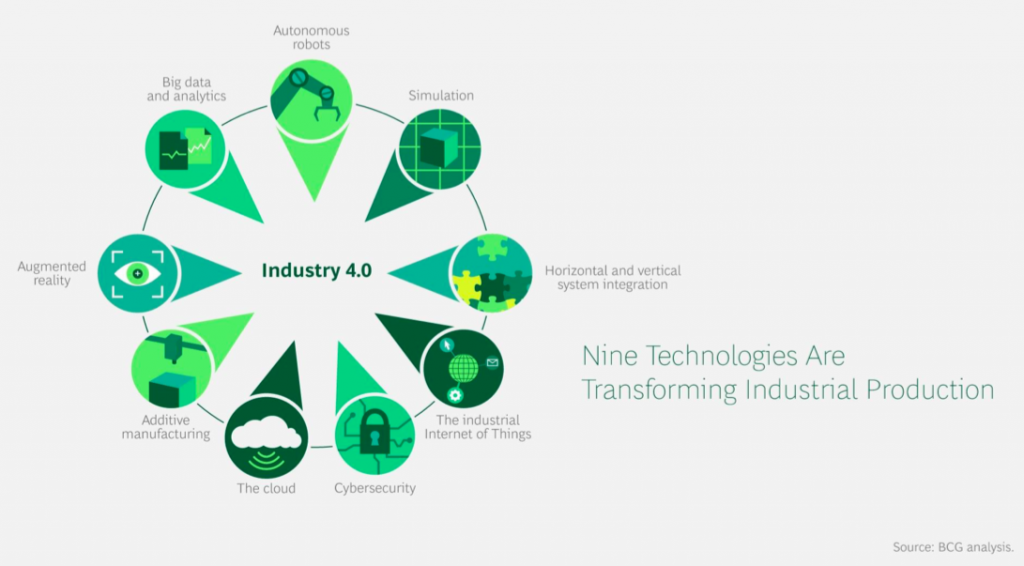
1. BIG DATA AND ANALYTICS
In an Industry 4.0 context, the collection and comprehensive evaluation of data from many different sources—production equipment and systems as well as enterprise- and customer-management systems—will become standard to support real-time decision making.
2. AUTONOMOUS ROBOTS
Robots will eventually interact with one another and work safely side by side with humans and learn from them. These robots will cost less and have a greater range of capabilities than those used in manufacturing today.
3. SIMULATION
Simulations will be used more extensively in plant operations to leverage real-time data and mirror the physical world in a virtual model, which can include machines, products, and humans. This will allow operators to test and optimize the machine settings for the next product in line in the virtual world before the physical changeover, thereby driving down machine setup times and increasing quality.
4. HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL SYSTEM INTEGRATION
With Industry 4.0, companies, departments, functions, and capabilities will become much more cohesive, as cross-company, universal data-integration networks evolve and enable truly automated value chains.
5. THE INDUSTRIAL INTERNET OF THINGS
Industry 4.0 means that more devices—sometimes including unfinished products—will be enriched with embedded computing. This will allow field devices to communicate and interact both with one another and with more centralized controllers, as necessary. It will also decentralize analytics and decision making, enabling real-time responses.
6. CYBERSECURITY
With the increased connectivity and use of standard communications protocols that come with Industry 4.0, the need to protect critical industrial systems and manufacturing lines from cybersecurity threats increases dramatically. As a result, secure, reliable communications as well as sophisticated identity and access management of machines and users are essential.
7. THE CLOUD
More production-related undertakings will require increased data sharing across sites and company boundaries. At the same time, the performance of cloud technologies will improve, achieving reaction times of just several milliseconds. As a result, machine data and functionality will increasingly be deployed to the cloud, enabling more data-driven services for production systems.
8. ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
Companies have just begun to adopt additive manufacturing, such as 3-D printing, which they use mostly to prototype and produce individual components. With Industry 4.0, these additive-manufacturing methods will be widely used to produce small batches of customized products that offer construction advantages, such as complex, lightweight designs.
9. AUGMENTED REALITY
Augmented-reality-based systems support a variety of services, such as selecting parts in a warehouse and sending repair instructions over mobile devices. These systems are currently in their infancy, but in the future, companies will make much broader use of augmented reality to provide workers with real-time information to improve decision making and work procedures.
Conclusion
Companies face formidable challenges in the adoption of these new technologies. To build and sustain a lead in the race to full implementation, they need to broaden and deepen their practical knowledge about digital technologies and the related use cases—and then develop and implement tailored digital manufacturing strategies.
Reports have even suggested that emerging markets like India could benefit tremendously from Industry 4.0 practices, and the city of Cincinnati, Ohio has declared itself an “Industry 4.0 demonstration city” to encourage investment and innovation in the manufacturing sector there.
The question, then, is not if Industry 4.0 is coming, but how quickly. As with big data and other business trends, I suspect that the early adopters will be rewarded for their courage jumping into this new technology, and those who avoid change risk becoming irrelevant and left behind.
Notes
Embracing Industry 4.0 and Rediscovering Growth
https://www.bcg.com/capabilities/operations/embracing-industry-4.0-rediscovering-growth.aspx
What Everyone Must Know About Industry 4.0
Why implementing Industry 4.0 is becoming an imperative


